Based on the latest U.S. Census, roughly 20% of Americans—about 62.8 million people—live in rural areas, from the Deep South to Midwestern farmlands to border towns out West. While rural life offers perks like a lower cost of living, less congestion, and star-filled skies, these benefits often come with limited healthcare options and other barriers to access.
And when it comes to cancer—cervical cancer, in particular—the trade-offs can mean life or death.
Although cancer death rates have declined nationwide, they remain higher and have decreased more slowly in rural areas compared to urban ones, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Cervical cancer death rates are especially high in some rural regions. In places like Appalachian Kentucky, they are nearly double the national average. A major reason? Women in these areas are more likely to be diagnosed at later stages, when the disease is harder to treat.
Behind these statistics are real women and families—with excessive wait times to see nearby doctors, lower human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination rates, and healthcare often clouded by stigma or medical bias. For National Public Health Week (April 6–12)—a time to advocate for health equity for all Americans—Cervivor, Inc. is digging into the complex challenge of reducing cervical cancer deaths in rural communities across the country.
These survivors’ stories underscore the urgency of addressing rural health disparities and the personal nature of this preventable disease—stories like Julianna’s.
Julianna’s Story

Six months before her 2020 cervical cancer diagnosis, Julianna Ferrone began experiencing symptoms such as bloating, bleeding, prolonged periods, and back pain. Living in Auburn, Alabama—a small college town with just one hospital and 300 doctors serving 11 counties—the 27-year-old had limited healthcare options and felt like she wasn’t being “taken seriously.” Making matters worse, many gynecologists in the area weren’t accepting new patients due to the pandemic. Her symptoms continued to worsen.
“After realizing I was not going to get the medical attention I needed locally due to limited resources, I found a doctor at the Georgia Cancer Center, over 100 miles away,” shares Julianna, who wrote a lengthy letter explaining her symptoms, concerns, and lack of access to care. The Georgia doctor saw her within two weeks.
During that first visit, the doctor gave Julianna a physical exam, noted her symptoms, and did an overdue cervical cancer screening. When the results came back abnormal, they developed a treatment plan that included four rounds of Cisplatin chemotherapy (to kill or slow cancer cells), 25 pelvic radiation treatments (to target cancer cells in the area), and two rounds of brachytherapy (internal radiation placed near the tumor). Before treatments could begin, however, Julianna required multiple surgeries.
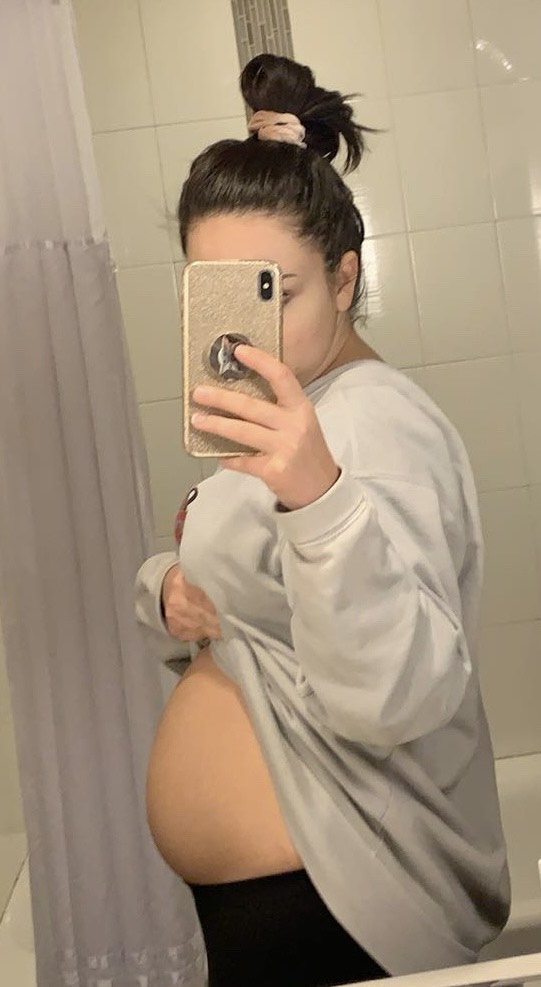

“The big belly photo was taken the day before my exploratory surgery when doctors removed my appendix because the cancer had spread there as well as endometriosis scar tissue,” says Julianna of this image of her bloated stomach. That same day, she underwent a colposcopy to examine her cervix for cancer, which returned abnormal results as well. Days later, she endured a four-hour hysterectomy that included the removal of multiple lymph nodes. On top of these grueling procedures and treatments, she spent countless hours commuting to Georgia from Alabama with her mother.
She has since experienced a recurrence and relocated to the Atlanta suburbs for better access to ongoing care. “Even living an hour outside Atlanta, there’s still a huge health disparity,” Julianna observes. “But I’m grateful to have surveillance appointments every three months at the cancer center.”
Today, the 2023 Cervivor School graduate advocates for awareness and prevention, lobbying state legislators, participating in American Cancer Society panels, and securing a gubernatorial proclamation recognizing Cervical Cancer Awareness Month in Georgia—a feat she was “ecstatic” about.
“This cancer is preventable—and we need to start talking about it,” she says, emphasizing that thousands of lives in Georgia could be saved through awareness. “There is such a stigma surrounding HPV and cervical cancer, especially in the South.”

Breaking Barriers to Care: Stigma and Bias
Since 1991, the CDC’s National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program (NBCCEDP) has provided free or low-cost mammograms and Pap tests to over 5.6 million women, detecting more than 57,000 breast cancer cases and 12,000 cervical cancer cases. Operating in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and several U.S. territories, the program collaborates with local health organizations to offer these life-saving services. Its goal? Reaching women at risk of delayed or skipped screenings.
Despite the public health program’s success, stigma remains—especially in some rural and conservative communities—where visiting a free clinic can lead to assumptions about a person’s financial or sexual health status.

Dr. Deanna Kepka, PhD, MPH, a researcher at the Huntsman Cancer Institute, works closely with rural and religious communities in Utah, including members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS). Speaking at Cervivor’s 2025 Cervical Cancer Summit, she described how stigma around sexual health often delays screenings and deters HPV vaccination.
She recalled working with Mandy Murray, a woman from a conservative LDS background who developed cervical cancer after experiencing sexual abuse. Although Mandy initially kept her diagnosis private, she eventually shared her story in 2018 through a book and on the Cervivor Blog, helping to raise awareness about cervical cancer screening and early detection as well as to show the power of breaking shame-induced silence.

Cervivor community member Claudia Pérez-Favela, who lives in California’s agricultural Imperial Valley, knows that stigma and bias can also exist within the medical system itself. Diagnosed with pre-cervical dysplasia caused by HPV in April 2018, she waited months to see a gynecologist while experiencing irregular periods and heavy bleeding. With a family history of ovarian cancer, Claudia chose to undergo a radical hysterectomy, including the removal of her ovaries. She was declared NED (No Evidence of Disease) just one month later.
But for Claudia, the hardest part wasn’t the wait—it was the care she received after her diagnosis. “From the moment I was diagnosed, I was met with judgment and misinformation,” she recalls. She was told her husband must have been unfaithful and faced other outdated assumptions. “The physician assistant didn’t explain my condition professionally—she let her personal bias take over because my cancer was HPV-related. Everything I now know about cervical cancer, I learned thanks to Cervivor.”
Living in a rural area made it difficult to find an alternate provider. She says, “When options are limited, you’re stuck with whoever is available—even if they’re overworked, unprofessional, or biased.” Today, Claudia often crosses the border into Mexico for more accessible, respectful care. “I can see a specialist there within a week.”
Turning the Tide on HPV Vaccination
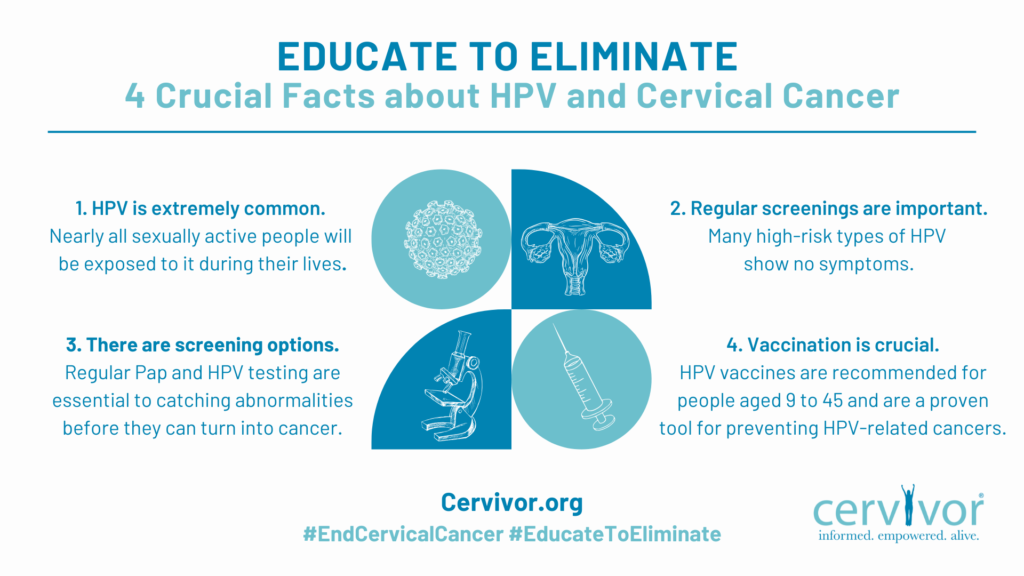
Research confirms that the HPV vaccine saves lives. In countries like Australia and Rwanda—where vaccination rates exceed 85% and 90%, respectively—cervical cancer is on the path to elimination.
The U.S. has a long way to go. In 2019, the CDC highlighted the “urgent need” to increase the national HPV vaccination rate to 80%, reporting that the vaccine could prevent up to 92% of HPV-related cancers, which still account for nearly 50,000 new cases annually, including about 12,000 cervical cancer cases. However, as of 2022, only 38.6% of children ages 9 to 17 in the U.S. had received at least one dose, according to a National Health Interview Survey. (Two doses of the vaccine are recommended for this age group, and three for those 18 and older.)
The same year, data showed disparities in HPV vaccination rates based on where kids lived: 40% of children in large metropolitan areas had received at least one dose, compared to just 30% in nonmetropolitan areas. Additionally, a 2025 study on overall childhood vaccination trends found that rural areas not only lag behind in vaccination rates but are also seeing slower increases compared to urban regions.

Despite ongoing challenges for vaccine advocates—and recent headlines about deadly measles outbreaks among unvaccinated children in rural Texas—there have also been notable successes.
In Utah, Dr. Kepka recounts how partnerships between the state health department and local providers have transformed HPV vaccination rates. “When I started working in Utah, we were always ranked 45th, 46th, or 47th in vaccination rates, and it was difficult to get healthcare team members on board,” she recalls.
Today, Utah leads the country, thanks largely to its vaccine registry, which identifies children eligible for vaccination as early as age 9. This proactive approach allows families to protect their children before puberty and becoming sexually active, making the vaccine an “easier pill to swallow” for LDS and other conservative families, Dr. Kepka explains.
Bringing Care Closer to Home

Beyond these barriers, one of the greatest challenges facing rural Americans in accessing care is often, quite literally, the distance to healthcare services, as survivor Julianna experienced.
Cervivor’s Community Engagement Liaison, Morgan Newman, who grew up in Greenfield, an Iowa town of 2,000, has experienced these disparities firsthand. “Specialists, including gynecologic oncologists, are limited, and patients face obstacles like transportation, lodging, time off work, and finances,” says Morgan, whose advocacy is rooted in her own cervical cancer diagnosis at age 24. “Iowa currently ranks second in overall cancer incidence, just behind Kentucky,” she says, citing both lifestyle and environmental factors such as high levels of radon. “It’s scary.”
Now working on the front lines of public health with Iowa experts, Morgan travels across the state to attend events ranging from school nurse conferences to HPV vaccination initiatives. She also serves on the Iowa Cancer Consortium Board of Directors and is committed to improving healthcare access, cervical cancer awareness, immunization education, and cancer policy.

Several promising solutions have been proposed to close the cervical cancer care gap in rural communities—and bring life-saving health services closer to home—though challenges remain in scaling these efforts:
- Expand Screening Options: New self-collection HPV tests offer a discreet and convenient way to get screened, helping to reduce barriers such as transportation and long appointment wait times. However, widespread adoption will require targeted education for patients, providers, and communities, particularly in rural areas.
- Increase Vaccine Access Points: Mobile vaccine clinics have proven successful when set up in accessible locations, such as Walmart parking lots on payday in Appalachian Kentucky. Utilizing pharmacies, school-based programs, dental offices, and providers through the CDC’s Vaccines for Children Program can bring vaccines closer to where families live, work, and shop.
- Leverage Telehealth: Follow-up care via telehealth allows patients to consult with providers without traveling long distances. While access to high-speed internet remains a challenge in some rural areas, many patients can still connect via cell phones, satellite service, or computers at local libraries.
Seeds of Hope: The Power of Rural Voices
“Storytelling and personal recommendations are key in rural areas,” one public health researcher shared with Cervivor. “Word-of-mouth is a powerful tool for spreading information.”
This is why Cervivor Founder and Chief Visionary, Tamika Felder, launched the organization 20 years ago. “I’ve always believed that sharing your story can change minds—and change the world,” she says. Since then, hundreds of survivors have shared their Cervivor Stories.
Reflecting on her experience with medical bias, California-based Cervivor Ambassador Claudia—now an active bilingual advocate in her rural community—believes survivors can educate healthcare providers. “HPV and cervical cancer are rarely discussed, leading to misinformation—even among healthcare workers. This fosters stigma, silence, and leaves women feeling isolated.” She adds, “Survivors can teach healthcare providers how clear, empathetic communication can make all the difference—or how its absence can cause harm.”

Utah-based Dr. Kepka stresses that women’s health is a community issue and needs community-driven solutions. “Don’t give up,” she encourages fellow health workers and advocates. “Keep sharing the facts—this is a ‘cancer-prevention vaccine’ or a ‘new approach for cervical cancer screening’—and be present in the community.”
Cervivor is equally committed to addressing health disparities and misinformation in rural areas through:
- Educational Outreach: The #Screen4Me campaign promotes life-saving cervical cancer screening and early detection nationwide. Through groups like Cervivor Español and initiatives like Cervivor Cares, we provide vital information to diverse communities using multilingual resources.
- Resource Support: Cervivor offers critical resources to underserved communities with initiatives like Cervivor Cares Gift Cards (for which you can nominate yourself or someone else or be sponsored) and the Comfort Care & Compassion Program (which can also be requested).
- Community Support: Creating Connections is a regular virtual support group that gives cervical cancer patients and survivors a safe, welcoming space to share, heal, and find community—from the comfort of home. Register for the May 2025 gathering.
- Credible Information: Through the Cervivor website, podcast, CervivorTV, and social media channels, we share actionable tips and public health guidance to help people stay informed about cervical cancer prevention.

Ultimately, planting seeds of hope—through individual stories and grassroots efforts—may offer the greatest potential for reducing cervical cancer death rates and ensuring that the next generation of rural Americans is free from HPV-related cancers, like cervical cancer.
Support the Mission!
Cervivor is leading the fight to eliminate cervical cancer here and around the globe. Support our mission through the Tell 20, Give 20 campaign, designed to spread awareness and continue to fund life-saving initiatives. (Read about the campaign’s success thus far and how to get involved.)
Have questions about this blog post or anything related to Cervivor or cervical cancer? Send them our way at [email protected]. Have your own Cervivor Story to share? Fill out this form, and we’ll be in touch!